Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Compare Fourier Model and T2* Model for 2D Stack of Spirals trajectory#
This examples walks through the elementary components of SNAKE.
Here we proceed step by step and use the Python interface. A more integrated
alternative is to use the CLI snake-main
# Imports
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from snake.core.simulation import SimConfig, default_hardware, GreConfig
from snake.core.phantom import Phantom
from snake.core.smaps import get_smaps
from snake.core.sampling import StackOfSpiralSampler
from mrinufft import get_operator
# For faster computation, try to use the GPU
NUFFT_BACKEND = "stacked-cufinufft"
COMPUTE_BACKEND = "cupy"
try:
import cupy as cp
if not cp.cupy.cuda.runtime.getDeviceCount():
raise ValueError("No CUDA Device found")
get_operator("cufinufft")
except Exception:
try:
get_operator("finufft")
except ValueError as e:
raise ValueError("No NUFFT backend available") from e
NUFFT_BACKEND = "finufft"
COMPUTE_BACKEND = "numpy"
print(
f"Using NUFFT backend: {NUFFT_BACKEND}", f"Using Compute backend: {COMPUTE_BACKEND}"
)
Using NUFFT backend: finufft Using Compute backend: numpy
sim_conf = SimConfig(
max_sim_time=3,
seq=GreConfig(TR=50, TE=22, FA=12),
hardware=default_hardware,
)
sim_conf.hardware.n_coils = 1 # Update to get multi coil results.
sim_conf.hardware.field_strength = 7
sim_conf.fov.res_mm = (3, 3, 3)
phantom = Phantom.from_brainweb(
sub_id=4, sim_conf=sim_conf, tissue_file="tissue_7T", output_res=1
)
phantom.masks.shape
(3, 181, 217, 181)
Setting up Acquisition Pattern and Initializing Result file.#
# The next piece of simulation is the acquisition trajectory.
# Here nothing fancy, we are using a stack of spiral, that samples a 3D
# k-space, with an acceleration factor AF=4 on the z-axis.
sampler = StackOfSpiralSampler(
accelz=1,
acsz=0.1,
orderz="top-down",
nb_revolutions=12,
obs_time_ms=30,
constant=True,
)
smaps = None
if sim_conf.hardware.n_coils > 1:
smaps = get_smaps(sim_conf.shape, n_coils=sim_conf.hardware.n_coils)
The acquisition trajectory looks like this
traj = sampler.get_next_frame(sim_conf)
from mrinufft.trajectories.display import display_3D_trajectory
display_3D_trajectory(traj)
<Axes3D: xlabel='kx', ylabel='ky', zlabel='kz'>
Adding noise in Image#
from snake.core.handlers.noise import NoiseHandler
noise_handler = NoiseHandler(variance=0.01)
Acquisition with Cartesian Engine#
The generated file example_EPI.mrd does not contains any k-space data for
now, only the sampling trajectory. let’s put some in. In order to do so, we
need to setup the acquisition engine that models the MR physics, and get
sampled at the specified k-space trajectory.
SNAKE comes with two models for the MR Physics:
model=”simple” :: Each k-space shot acquires a constant signal, which is the image contrast at TE.
model=”T2s” :: Each k-space shot is degraded by the T2* decay induced by each tissue.
# Here we will use the "simple" model, which is faster.
#
# SNAKE's Engine are capable of simulating the data in parallel, by distributing
# the shots to be acquired to a set of processes. To do so , we need to specify
# the number of jobs that will run in parallel, as well as the size of a job.
# Setting the job size and the number of jobs can have a great impact on total
# runtime and memory consumption.
#
# Here, we have a single frame to acquire with 60 frames (one EPI per slice), so
# a single worker will do.
from snake.core.engine import NufftAcquisitionEngine
# engine = NufftAcquisitionEngine(model="simple", snr=30000, slice_2d=True)
# engine(
# "example_spiral_2D.mrd",
# sampler,
# phantom,
# sim_conf,
# handlers=[noise_handler],
# smaps=smaps,
# worker_chunk_size=60,
# n_workers=1,
# nufft_backend=NUFFT_BACKEND,
# )
engine_t2s = NufftAcquisitionEngine(model="T2s", snr=30000, slice_2d=True)
engine_t2s(
"example_spiral_t2s_2D.mrd",
sampler,
phantom,
sim_conf,
handlers=[noise_handler],
worker_chunk_size=60,
n_workers=1,
nufft_backend=NUFFT_BACKEND,
)
Using 2D acquisition, the TR_eff is updated to TR_vol
Existing example_spiral_t2s_2D.mrd it will be overwritten
0%| | 0/60 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
60%|██████ | 36/60 [00:00<00:00, 331.99it/s]
100%|██████████| 60/60 [00:00<00:00, 395.25it/s]
/volatile/github-ci-mind-inria/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xsdata/formats/dataclass/parsers/utils.py:126: ConverterWarning: Failed to convert value for `waveformInformationType.waveformType`
`56449` is not a valid `waveformInformationTypeWaveformType`
warnings.warn(message, ConverterWarning)
No coil_cov found in the dataset.
0%| | 0/60 [00:00<?, ?it/s]/volatile/github-ci-mind-inria/gpu_mind_runner/_work/_tool/Python/3.10.16/x64/lib/python3.10/site-packages/mrinufft/_utils.py:94: UserWarning: Samples will be rescaled to [-pi, pi), assuming they were in [-0.5, 0.5)
warnings.warn(
/volatile/github-ci-mind-inria/gpu_mind_runner/_work/_tool/Python/3.10.16/x64/lib/python3.10/site-packages/mrinufft/_utils.py:94: UserWarning: Samples will be rescaled to [-pi, pi), assuming they were in [-0.5, 0.5)
warnings.warn(
100%|██████████| 60/60 [00:06<00:00, 8.90it/s]
100%|██████████| 60/60 [00:07<00:00, 8.06it/s]
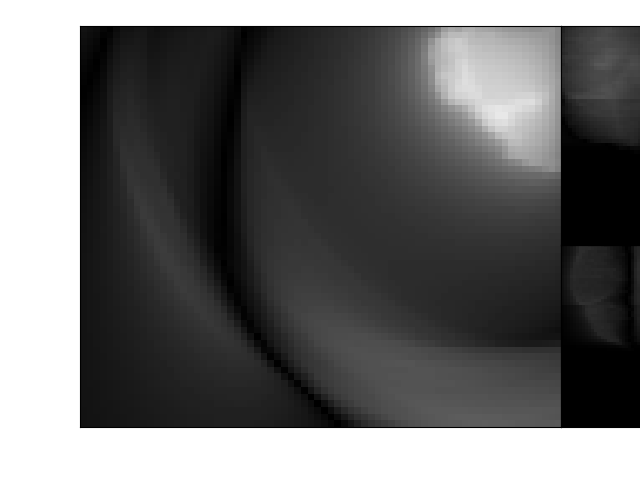
from snake.mrd_utils import NonCartesianFrameDataLoader
from snake.toolkit.plotting import axis3dcut
with NonCartesianFrameDataLoader("example_spiral_t2s_2D.mrd") as data_loader:
traj, kspace_data = data_loader.get_kspace_frame(0, shot_dim=True)
/volatile/github-ci-mind-inria/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xsdata/formats/dataclass/parsers/utils.py:126: ConverterWarning: Failed to convert value for `waveformInformationType.waveformType`
`56449` is not a valid `waveformInformationTypeWaveformType`
warnings.warn(message, ConverterWarning)
kspace_data = kspace_data.squeeze()
shot = traj[18].copy()
nufft = get_operator(NUFFT_BACKEND)(
samples=shot[:, :2],
shape=data_loader.shape[:-1],
density=None,
n_batchs=len(kspace_data),
)
nufft.samples = shot[:, :2]
image = nufft.adj_op(kspace_data)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
axis3dcut(abs(image), None, cuts=(40, 40, 40), ax=ax)

/volatile/github-ci-mind-inria/gpu_mind_runner/_work/_tool/Python/3.10.16/x64/lib/python3.10/site-packages/mrinufft/_utils.py:94: UserWarning: Samples will be rescaled to [-pi, pi), assuming they were in [-0.5, 0.5)
warnings.warn(
(<Figure size 640x480 with 5 Axes>, <Axes: >, (40, 40, 40))
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 32.304 seconds)

