Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Create a GRE Sequence using Pulseq#
Example how to create sequences using PyPulseq.
import numpy as np
from mrinufft.trajectories.display import display_3D_trajectory
from mrinufft.trajectories import initialize_2D_spiral, stack
from mrinufft.io.pulseq import pulseq_gre, read_pulseq_traj
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Defining the sequence parameters like repetition time (TR), echo time (TE), flip angle (FA), field-of-view (FOV) and image matrix size.
Create a stack of spiral for our trajectory
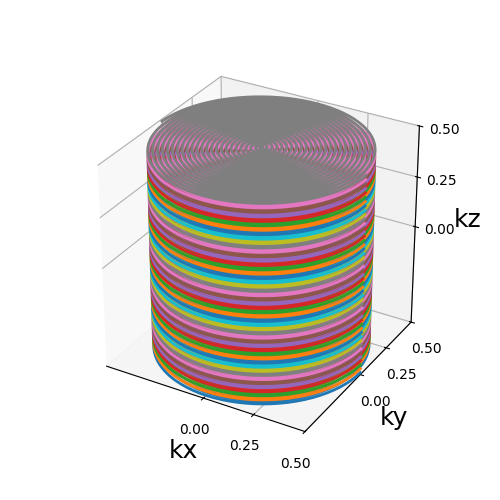
<Axes3D: xlabel='kx', ylabel='ky', zlabel='kz'>
/volatile/github-ci-mind-inria/gpu_mind_runner/_work/mri-nufft/mri-nufft/.venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pypulseq/make_block_pulse.py:80: UserWarning: Using default 4 ms duration for block pulse.
warn('Using default 4 ms duration for block pulse.')
0it [00:00, ?it/s]3
1
1
3
3
1
1
1
1
1
9it [00:00, 161.42it/s]
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0it [00:00, ?it/s]3
1
1
3
3
7
1it [00:00, 9.56it/s]1
1
1
1
9it [00:00, 74.44it/s]
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
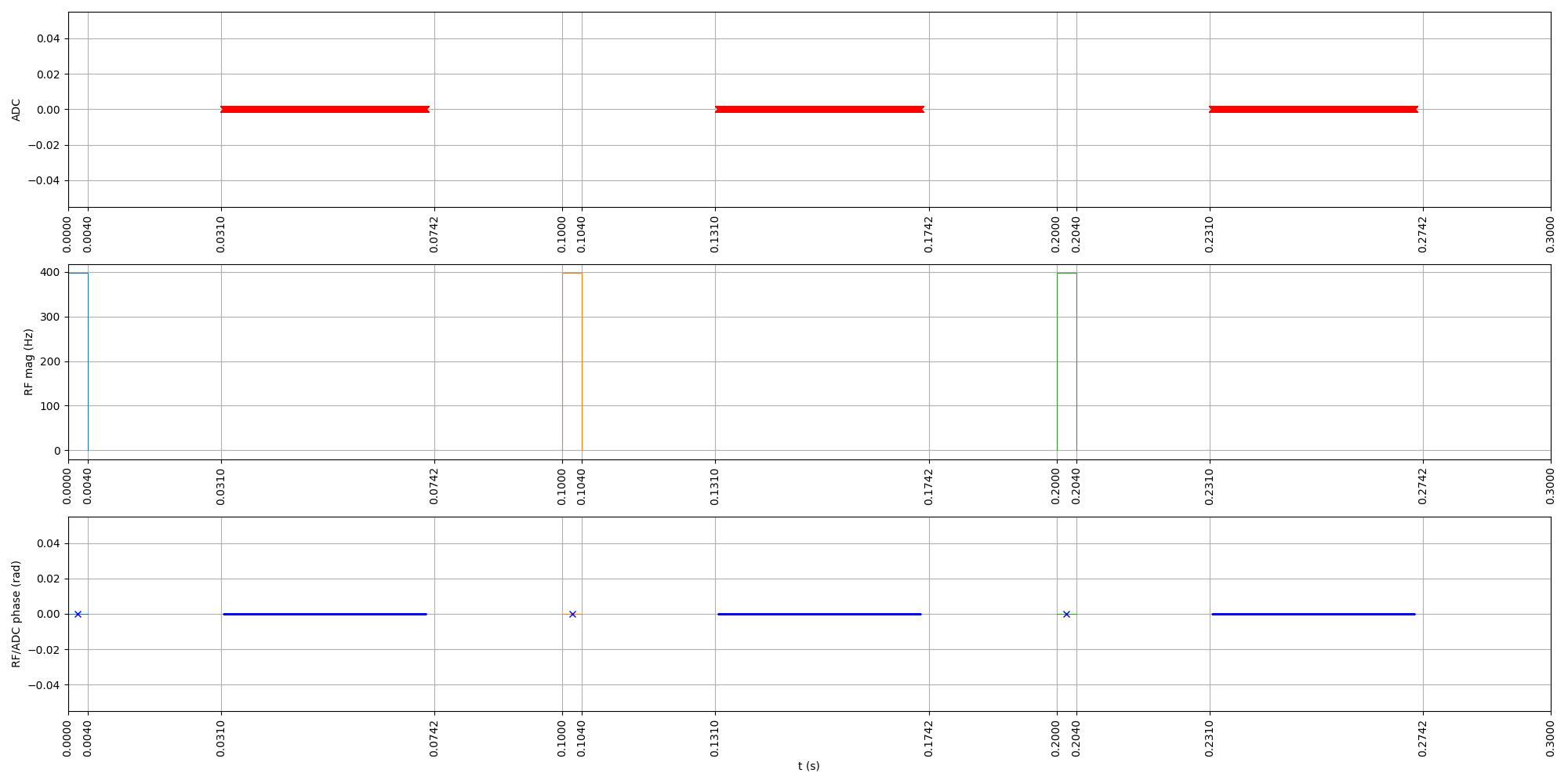
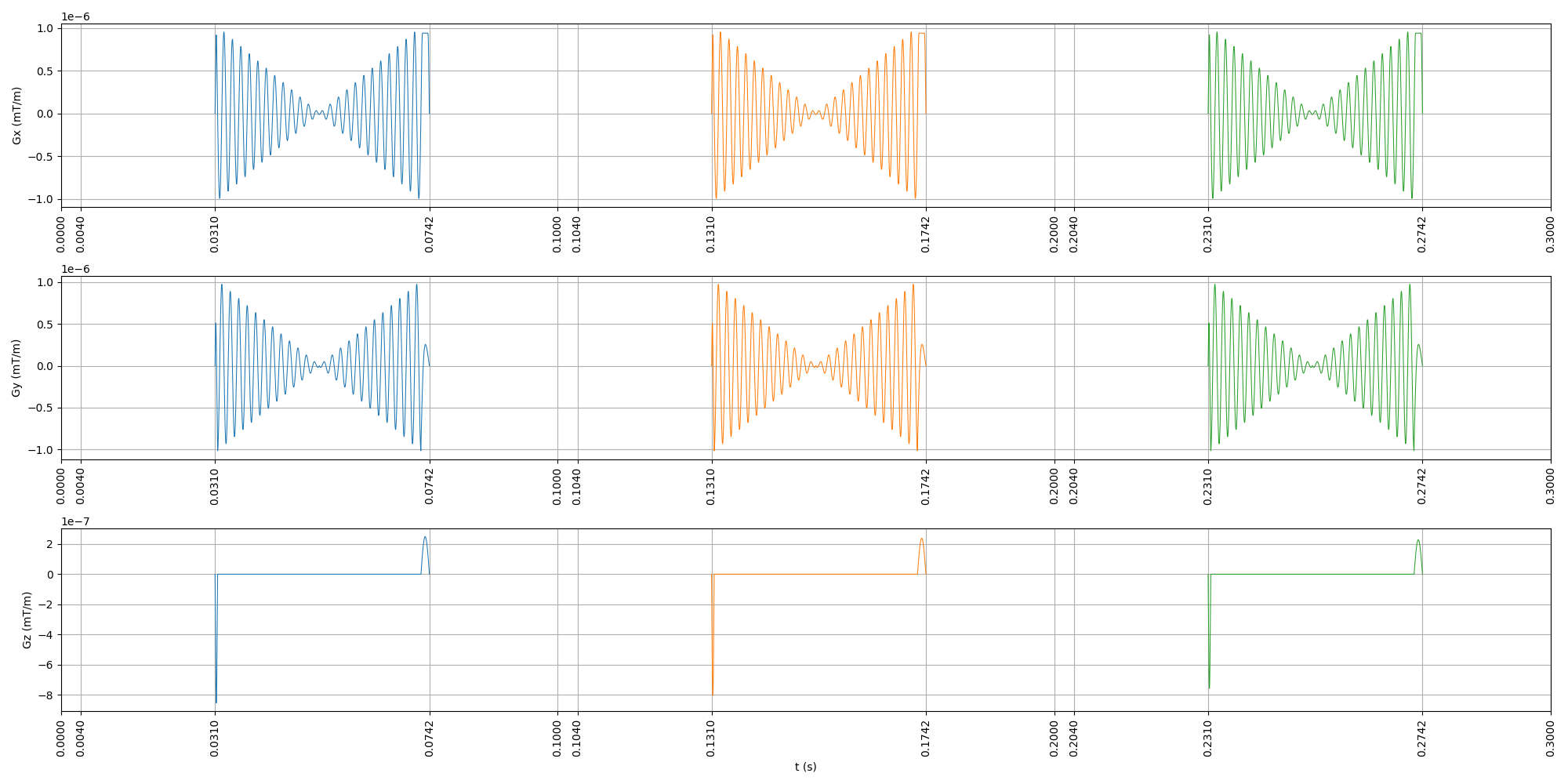
# Let's show the sequence.
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (20, 10)
seq.plot(show_blocks=True, grad_disp="mT/m")
<pypulseq.utils.seq_plot.SeqPlot object at 0x7a5537b9f5b0>
read_kspace = read_pulseq_traj(seq)
KMAX = 0.5
kspace_adc, _, t_exc, t_refocus, t_adc = seq.calculate_kspace()
# split t_adc with t_exc and t_refocus, the index are then used to split kspace_adc
FOV = seq.get_definition("FOV")
t_splits = np.sort(np.concatenate([t_exc, t_refocus]))
idx_prev = 0
kspace_shots = []
for t in t_splits:
idx_next = np.searchsorted(t_adc, t, side="left")
if idx_next == idx_prev:
continue
kspace_shots.append(kspace_adc[:, idx_prev:idx_next].T)
if idx_next == kspace_adc.shape[1] and t > t_adc[-1]: # last useful point
break
idx_prev = idx_next
if idx_next < kspace_adc.shape[1]:
kspace_shots.append(kspace_adc[:, idx_next:].T) # add remaining gradients.
# convert to KMAX standard.
kspace_shots = np.ascontiguousarray(kspace_shots) * KMAX * 2 * np.asarray(FOV)
and we can display the k-space trajectory, loaded from the sequence file.
display_3D_trajectory(kspace_shots)
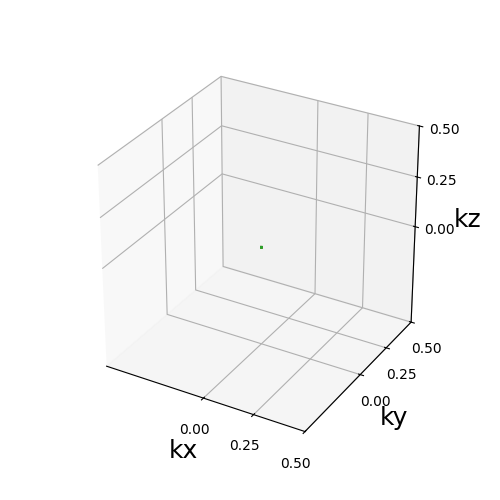
<Axes3D: xlabel='kx', ylabel='ky', zlabel='kz'>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.481 seconds)