Note
Go to the end to download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Reconstruction with conjugate gradient#
An example to show how to reconstruct volumes using conjugate gradient method.
This script demonstrates the use of the Conjugate Gradient (CG) method for solving systems of linear equations of the form \(Ax = b\), where \(A`\) is a symmetric positive-definite matrix. The CG method is an iterative algorithm that is particularly useful for large, sparse systems where direct methods are computationally expensive.
The Conjugate Gradient method is widely used in various scientific and engineering applications, including solving partial differential equations, optimization problems, and machine learning tasks.
This method is inspired by techniques from [SigPy] and [Aquaulb] MOOC, as well as general knowledge in [Wikipedia].
Imports
import numpy as np
import cupy as cp
import mrinufft
from brainweb_dl import get_mri
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import os
BACKEND = os.environ.get("MRINUFFT_BACKEND", "gpunufft")
Setup Inputs
Setup the NUFFT operator
NufftOperator = mrinufft.get_operator(BACKEND) # get the operator
nufft = NufftOperator(
samples_loc,
shape=image.shape,
density=True,
squeeze_dims=True,
) # create the NUFFT operator
/volatile/github-ci-mind-inria/gpu_mind_runner/_work/mri-nufft/venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/mrinufft/_utils.py:76: UserWarning: Samples will be rescaled to [-pi, pi), assuming they were in [-0.5, 0.5)
warnings.warn(
/volatile/github-ci-mind-inria/gpu_mind_runner/_work/mri-nufft/venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/mrinufft/_utils.py:81: UserWarning: Samples will be rescaled to [-0.5, 0.5), assuming they were in [-pi, pi)
warnings.warn(
Reconstruct the image using the CG method
kspace_data_gpu = nufft.op(image_gpu) # get the k-space data
kspace_data = kspace_data_gpu.get() # convert back to numpy array for display
dc_adjoint = nufft.adj_op(kspace_data_gpu) # density compensated adjoint NUFFT
reconstructed_image, loss = nufft.cg(
kspace_data=kspace_data_gpu,
x_init=dc_adjoint.copy(),
num_iter=50,
compute_loss=True,
)
# convert back to numpy array for display
reconstructed_image = reconstructed_image.get().squeeze()
# Display the results
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
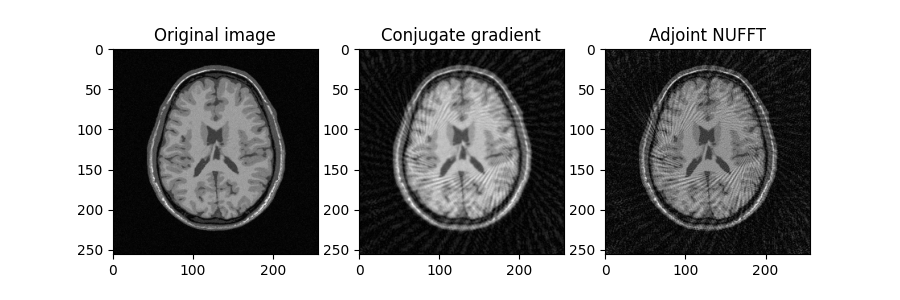
plt.subplot(2, 3, 1)
plt.title("Original image")
plt.imshow(image, cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar()
plt.subplot(2, 3, 2)
plt.title("Conjugate gradient")
plt.imshow(abs(reconstructed_image), vmin=image.min(), vmax=image.max(), cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar()
plt.subplot(2, 3, 3)
plt.title("Adjoint NUFFT")
plt.imshow(
abs(nufft.adj_op(kspace_data)),
vmin=image.min(),
vmax=image.max(),
cmap="gray",
)
plt.colorbar()
plt.subplot(2, 3, 4)
plt.title("Loss")
plt.plot(loss.get())
plt.grid()
plt.subplot(2, 3, 5)
plt.title("K-space from conjugate gradient (CG)")
plt.plot(np.log(abs(kspace_data)), label="Acquired k-space")
plt.plot(np.log(abs(nufft.op(reconstructed_image))), label="CG k-space")
plt.legend(loc="lower left", fontsize=8)
plt.subplot(2, 3, 6)
plt.title("K-space from DC adjoint NUFFT")
plt.plot(np.log(abs(kspace_data)), label="Acquired k-space")
plt.plot(np.log(abs(nufft.op(dc_adjoint).get())), label="DC adjoint k-space")
plt.legend(loc="lower left", fontsize=8)
/volatile/github-ci-mind-inria/gpu_mind_runner/_work/mri-nufft/venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/mrinufft/operators/base.py:857: UserWarning: Lipschitz constant did not converge
warnings.warn("Lipschitz constant did not converge")
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7306ec324bb0>
References#
SigPy Documentation. Conjugate Gradient Method. https://sigpy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/_modules/sigpy/alg.html#ConjugateGradient
Aquaulb’s MOOC: Solving PDE with Iterative Methods. https://aquaulb.github.io/book_solving_pde_mooc/solving_pde_mooc/notebooks/05_IterativeMethods/05_02_Conjugate_Gradient.html
Wikipedia: Conjugate Gradient Method. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conjugate_gradient_method
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.279 seconds)
